What Is a Bill of Entry (BOE)? Complete Guide with BOE Status Meaning, IGST Process & Mistakes
A Bill of Entry (BOE) is the mandatory legal document filed by importers or their customs agent (CHA) when goods arrive at an Indian Sea Port/ Land Port/ Airport. It serves as the official declaration to customs, it contains detailed information about type, quantity, value, and classification of imported goods. Without a valid BOE, customs cannot clear your shipment, no duties or taxes can be assessed, and goods remain stuck at the port indefinitely. Importers can track the progression of BOE using the Icegate portal. Understanding what Bill of Entry is and how to track its status on Icegate is critical for timely customs clearance.
What Is a Bill of Entry (BOE)?
A Bill of Entry (BOE) is fundamentally a customs clearance declaration. The main purpose of BOE is the assessment of customs duty. When imported goods arrive at an Indian Sea port, Airport, or Inland port, the importer or their authorized Customs House Agent (CHA) must file a BOE with customs authorities for the timely clearance of goods.
BOE vs. Bill of Lading (B/L): Understanding the Difference
Many importers confuse Bill of Entry (BOE) with Bill of Lading (B/L). These are completely different documents. Below are some of the major differences:
Types of Bill of Entry: Which One Do You Need?
BOEs are categorized based on what you intend to do with the imported goods. Understanding which type applies to your shipment is critical because filing the wrong type can delay clearance.
Type 1: BOE for Home Consumption (Most Common)
BOE filed for goods intended for immediate domestic use and consumption in India.This is your default BOE type if you're importing goods to sell domestically, use in your business, or manufacture further products. You pay full customs duties, IGST, and other applicable taxes immediately.
Type 2: BOE for Warehousing (Bonded Warehouse)
BOE filed for goods that will be stored in a government-approved bonded warehouse temporarily, with duty payment deferred. Duties are NOT paid during warehousing. You pay only when goods are released from the warehouse.
Type 3: BOE for Ex-Bond Clearance
BOE is filed when goods stored in a bonded warehouse are released for domestic consumption. Full duties and taxes paid at this point.
Type 4: BOE for Re-Export
BOE filed for goods being re-exported (imported and then exported again without modification). Special schemes like DFIA (Duty Free Import Authorization) or EPCG may apply.
The Bill of Entry Format
Understanding BOE format helps you understand what information customs needs and why. Below is a BOE (Home Consumption) Format.
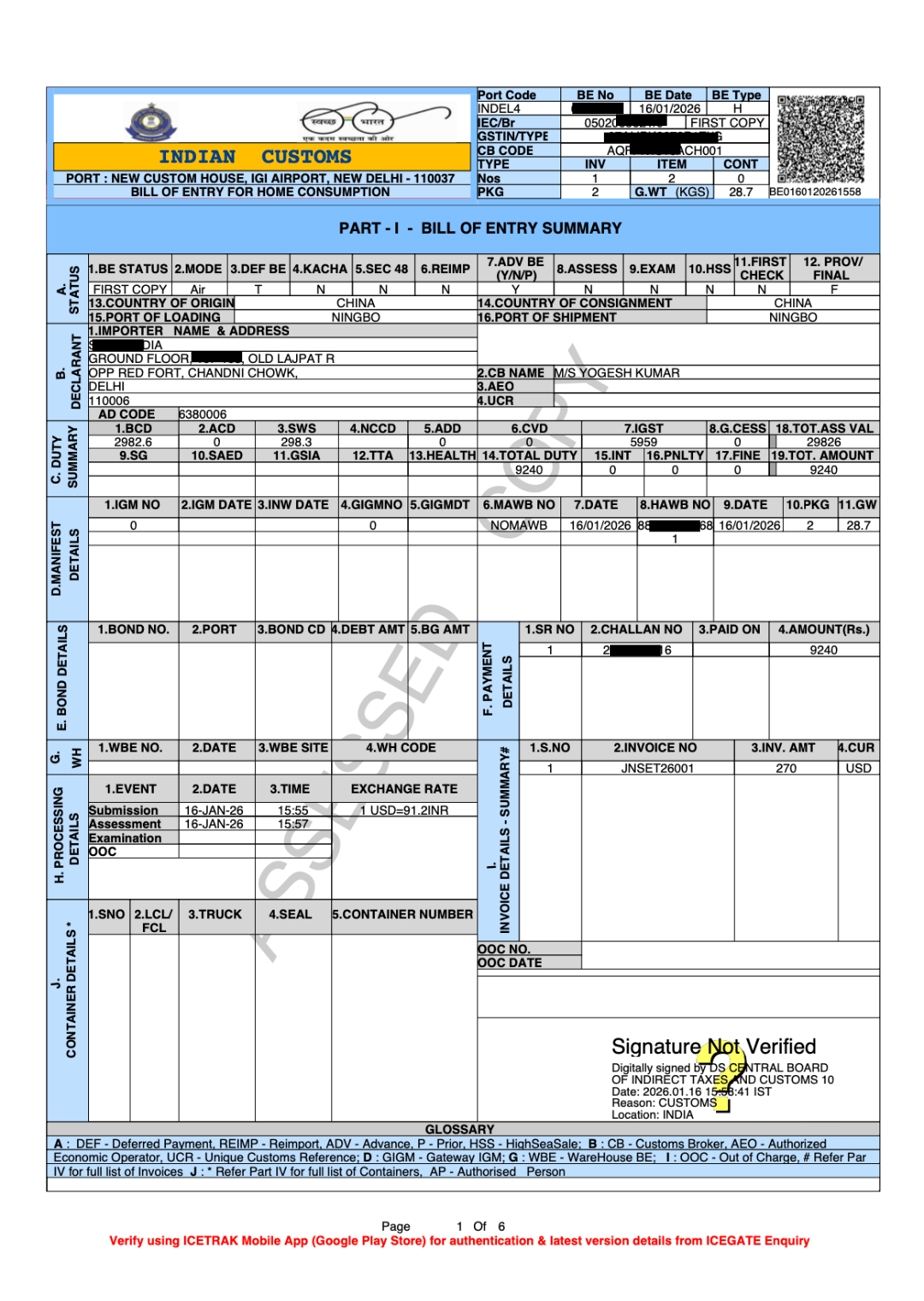
Bill of Entry Status: Understanding BOE Status on Icegate
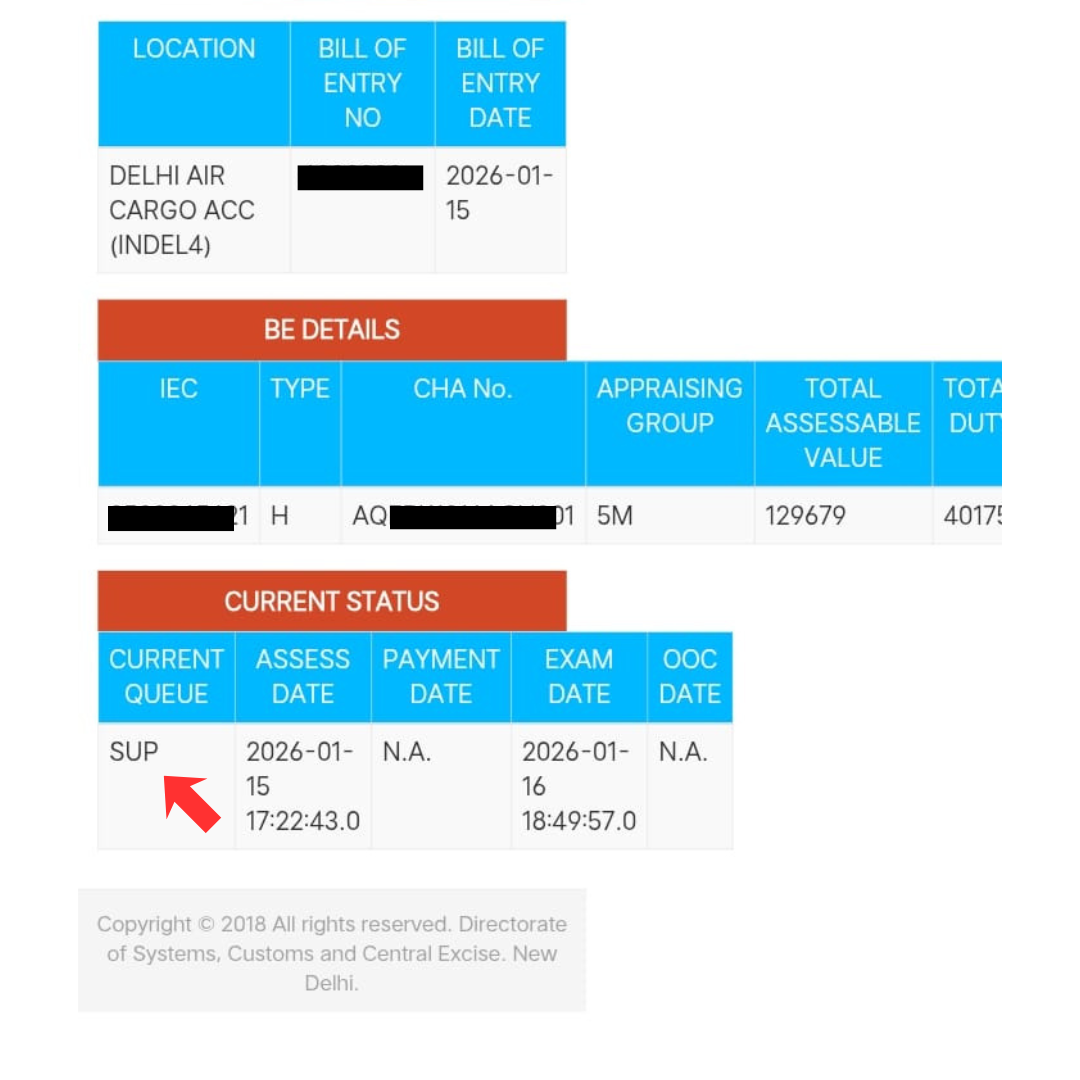
Your shipment's BOE goes through several statuses as customs processes it. Tracking Bill of Entry status on ICEGATE is crucial because it tells you exactly where your shipment stands and when you can collect it.
The Four Main BOE Status Types
Status 1: "Under Assessment"
Customs is currently reviewing your BOE, checking document accuracy, and verifying HS codes and duty calculations.
Status 2: "Assessment Complete" (or "Duty Assessed")
Customs has verified all details and calculated the exact duties and taxes you must pay. Pay duties immediately through Icegate portal channels. Delay in payment attracts interest on duty and demurrage charges.
Status 3: "Out of Charge" (Clearance Complete)
CUSTOMS HAS FULLY CLEARED YOUR SHIPMENT. All documents are verified, duty and taxes are paid, goods have been examined (if required) and now ready for collection.
Status 4: "Query Raised" or "Pending Clarification"
Customs has questions or concerns about your shipment and needs additional information before clearing it. For example:
- HS code discrepancy
- Value mismatch
- Missing or incomplete documents
- Restricted item classification confusion
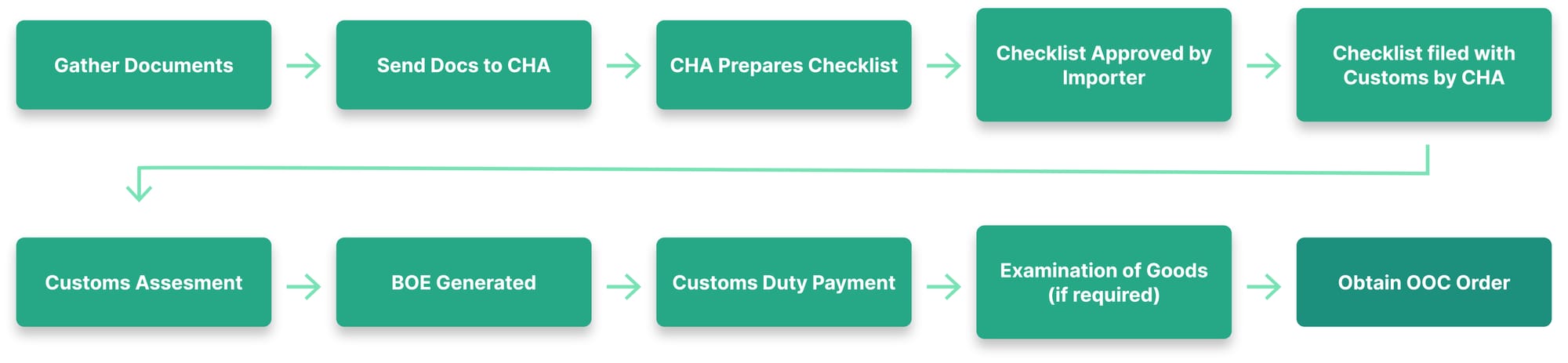
Bill of Entry Filing Process: How It Actually Works
Understanding the complete BOE filing process helps you anticipate what to expect and prepare documents in advance.
Pre-Filing: Document Preparation
Before your CHA files the BOE, you must provide:
- Commercial Invoice
- Packing List
- Bill of Lading (B/L)
- Import License (if restricted)
- Certificate of Origin
- Insurance Certificate
- IEC Copy
- GSTIN Certificate
- CHA Authorization Letter
The following is an overview of some of the key steps involved in a Bill of Entry filing:
Common BOE Mistakes That Cause Delays & How to Avoid Them
Mistake #1: Wrong HS Code Classification
You declared mobile phones under HS code 8517.62.10 (smartphones) but they're actually feature phones, which fall under 8517.62.90 (different duty rate).
Mistake #2: Declaring Low Value to Reduce Duty
Your invoice shows $20,000 value, but you declare $15,000 to ICEGATE to reduce duty.
Mistake #3: Incomplete or Wrong Importer Details
BOE filed with incorrect GSTIN or IEC number. Customs can't verify your registration.
Mistake #4: Missing Import License for Restricted Items
Your product requires an import license (e.g., electronic components) but you file BOE without license.
Mistake #5: Inconsistent Documentation
- Invoice shows 100 units, Packing list shows 95 units, BOE declares 100 units
- Invoice value is $20,000 but B/L shows different CIF
- Product description varies between documents
BOE and GST Integration: Claiming Input Tax Credit (ITC)
One major reason BOE matters for GST purposes is that it's your gateway to claiming input tax credit (ITC) on imported goods.
How BOE Links to GST ITC
When you import goods:
- You pay IGST at customs (on imported goods)
- BOE is filed with your GSTIN
- ICEGATE shares BOE data with GST system
- GST system automatically populates GSTR-2A (purchase return)
- You claim ITC on IGST paid
- Reduces your GST liability
Example:
Shipment Value: ₹10 lakh
Basic Customs Duty (15%): ₹1.5 lakh
IGST (18% on ₹11.5L): ₹2.07 lakh
Total Tax Paid: ₹3.57 lakh
GST ITC Claimable: ₹2.07 lakh
Net Cost: ₹11.5 lakh (after ITC)
BOE Status FAQ: Quick Answers to Common Questions
Q: How long does BOE clearance take?
A: Typically 5-7 working days from port arrival for sea shipments and 1-2 days for air shipments.
Q: Can I collect goods before BOE status shows "Out of Charge"?
A: No. Goods cannot be released until BOE shows "Out of Charge" status. It's a legal requirement.
Q: Can I check BOE status without IEC?
A: No. You need either your IEC or BOE number to check status.
Q: What happens if BOE is not cleared within 30 days?
A: After 60 days, if BOE is not cleared and duties not paid, goods can be auctioned by customs.
Q: Can I amend BOE after goods are cleared?
A: Technically yes, but there's no benefit. After clearance, amendments require officer approval and become complex.
Q: If my goods are physically examined, does it delay clearance?
A: Examination adds 1-3 days. After examination, if goods match BOE, clearance proceeds normally.
Q: Can I track BOE without ICEGATE account?
A: No, Public tracking has been discontinues. You will need a Icegate login to track BOE.
Conclusion
The Bill of Entry (BOE) is the backbone of import compliance in India. It ensures legal clearance of goods, accurate duty assessment, and regulatory compliance with customs, RBI, and DGFT.
Whether you are a first-time importer or an established trader, understanding BOE meaning, types, and filing process is essential for smooth international trade operations.